Your body is always working whether you are resting or sleeping. Normal body functions like breathing, circulating blood, repairing cells and controlling body temperature help in keeping your organs working properly. This happens naturally inside your body and is carried out by metabolism, which keeps these life-sustaining activities going.
People often ask what metabolism is and how it is related to weight loss and calorie burning. But to the amazement, it has a much bigger effect on your overall health.It changes how much energy you have, how quickly you recover, how well your hormones work, and how well your body adapts to daily tasks. Learning about metabolism can help you understand how your body really works.
What Is Metabolism?
The process of metabolism carries on continuously. It converts the food and drink that enters your body and provides energy to keep it alive through all its functions, whether simple, like respiration and digestion, or complex as moving, thinking, or healing.
Thousands of biochemical reactions occur in your cells every moment of the day. The biochemical reactions are what break down food particles, give off fuel energy, and support the body in the repair of damage to the tissues, balance hormones, etc., thus maintaining homeostasis.
Types Of Metabolism?
Catabolism is the part of metabolism that breaks down the food you eat into smaller molecules that your body can use. Your body doesn’t use carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in the same way they are when you eat them. Instead, it turns them into glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids. There are two types of metabolism:
1. Catabolism: Breaking Down Nutrients for Energy
Catabolism is the element of metabolism that breaks down the food you ingest into smaller pieces that your body can use. Your body doesn’t use carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the same way as they are when you eat them. It breaks them down into glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids instead.
This breakdown gives off energy, which your body uses to:
- Give physical movement power
- Help with digestion
- Keep the brain working
- Feed important organs
During catabolism, the liver and muscles can store additional energy as glycogen or fat for later use. When the body needs energy quickly, such as when you’re unwell, fasting, or working out, catabolism is more active and works harder.
2. Anabolism: Building, Repairing, and Storing Energy
Anabolism is the part of metabolism that makes things. It uses the energy from breaking down substances to grow and repair tissues all across the body. This includes:
- Building muscular tissue
- Repairing cells that have been harmed
- Making hormones and enzymes
- Helping bones grow and get better
When you are recovering, relaxing, growing, pregnant, or after working out, anabolism is essential. Without anabolism, the body wouldn’t be able to recover, get stronger, or deal with stress.
A healthy metabolism needs a balance between breaking down and building up. Too much breakdown without repair can make the body weaker, and too much building without balance can cause unwanted weight gain.
Function Of Metabolism
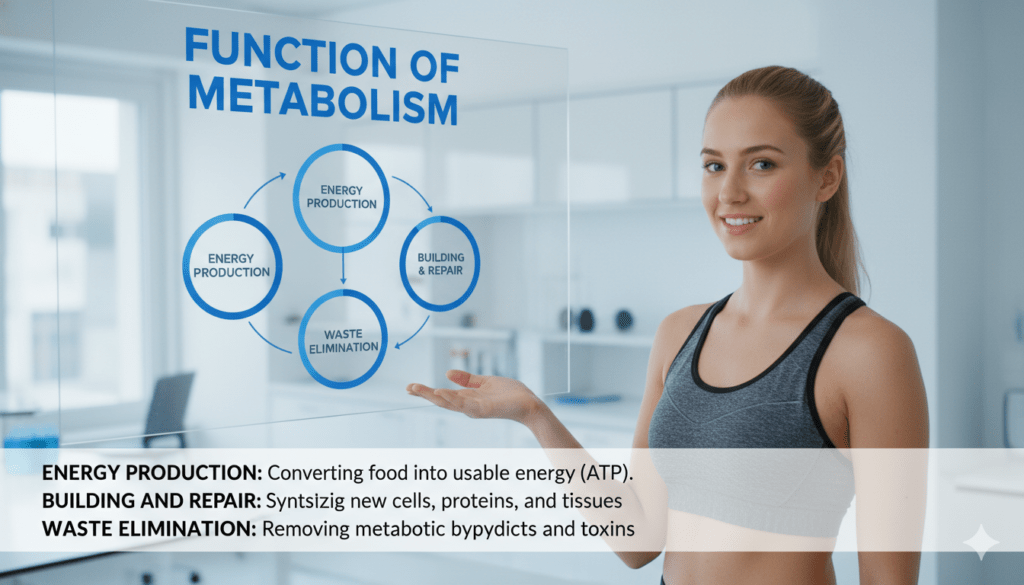
Metabolism is the process by which your body uses the energy from the food you eat and drink to do everything. It works all the time, even when you’re sleeping or resting.
Your metabolism keeps your body going by helping with important things like breathing and moving blood around.
- Digesting food and taking in nutrients
- Fixing and growing cells
- Hormones in balance
- Keeping your body temperature stable
A healthy metabolism is also adaptable. Depending on what’s going on, like eating, working out, fasting, recovering from an illness, or even being pregnant, it changes how much energy your body uses.
This means that metabolism doesn’t work at a set speed. It can speed up or slow down depending on what your body needs at different times of the day or when your environment or lifestyle changes.
The Role of Metabolic Rate
When people talk about metabolism in ordinary life, they frequently refer to metabolic rate, which simply means how quickly your body uses energy.
- Metabolic rate affects how many calories your body burns daily.
- How effectively are nutrients utilized?
- How are energy levels maintained?
A greater metabolic rate indicates that the body consumes more energy even when resting, whereas a lower metabolic rate means that fewer calories are required to satisfy daily demands. This rate varies from person to person and fluctuates with time.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is how much of energy your body utilizes for performing important functions such as breathing, blood circulation, organ function, and temperature regulation.
Consider it your body’s engine idling in the background, operating continuously even when you’re sleeping. BMR accounts for the majority of your daily calorie intake, around 60-75%, and is an important element of knowing how metabolism works and how your body consumes energy throughout the day.
How to calculate BMR?
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is the number of calories your body needs to perform basic life-sustaining functions while at complete rest. This includes breathing, circulating blood, regulating body temperature, and supporting organ function.
BMR Calculation Formula
The most widely used and reliable method is the Harris-Benedict equation.
For Men:
BMR = 88.36 + (13.4 × weight in kg) + (4.8 × height in cm) − (5.7 × age in years)
For Women:
BMR = 447.6 + (9.2 × weight in kg) + (3.1 × height in cm) − (4.3 × age in years)
Factors That Influence Metabolism
Metabolism is affected by several internal and external factors, and this is the reason why people have different metabolism rates. It is usually affected by:
Key factors include:
- Age: Metabolism naturally slows with age
- Muscle mass: More muscle increases energy use
- Physical activity: Movement boosts metabolic activity
- Hormonal balance: Thyroid hormones strongly affect metabolism
- Diet patterns: Long-term calorie restriction can slow metabolism
All these factors together are responsible for how efficiently your body is using energy.
How Metabolism Affects Body Weight?
Metabolism plays an important role in maintaining a healthy weight, and at which you are gaining or losing weight. There is a very basic thing: when you eat more calories than you burn, your weight gets affected, and your body starts storing fat. A healthy metabolism helps your body:
- Use energy wisely
- Keep your energy levels steady all day long
- Make sure you process nutrients well
Other lifestyle factors, such as how well you sleep, how stressed you are, what you eat, and how much you exercise, also have a big effect on your weight. This means that your daily habits and choices have a big effect on how your body gains or loses weight, even if your metabolism is working well.
Metabolic Disorders: When Metabolism Is Disrupted?
The body’s metabolism may sometimes be inefficient and not function as it should; this can lead to metabolic diseases. A metabolic disease occurs when the body is unable to metabolize certain nutrients, produce adequate energy, or maintain a balance between nutrient intake and activity level.
There are a number of different reasons that may contribute to the development of metabolic disease. Some of the most common reasons include:
- Hormonal changes in the body, such as thyroid being too high or too low, affect the body’s natural metabolism rate.
- Enzyme deficiencies or certain inherited conditions like phenylketonuria, which is generally caused when the body is not able to break down certain proteins.
- Nutritional deficiencies, such as low iron or vitamin D levels, will affect energy levels and health
- The effect of medications or the presence of toxins can impact normal metabolic function
Metabolic diseases are of various types,s and they can not be described in a single word. Common conditions like diabetes, thyroid diseases, metabolic syndrome, and some conditions that are inherited from the family. It is important to first identify these diseases and treat them accordingly.
How To Keep A Healthy Metabolism Naturally?
Your genes play an important role in your body’s metabolism. But apart from that, small activities like your daily life choices such as your diet, your physical routine also affect the metabolism rate and how well it works. You can help your body keep a steady flow of energy, process nutrients well, and support overall metabolic balance by following healthy habits. Some helpful things to do are:
- Eating balanced meals regularly
- Including adequate protein
- Staying physically active
- Prioritizing quality sleep
- Drinking enough water
- Avoiding extreme dieting
These habits help keep energy production steady and the metabolism in balance.
Conclusion
When you know your metabolism, how your body produces energy, adapts to changes, and balances itself through metabolism, you will gain insight into how these processes work. Metabolism supports every important function of the body, not just weight-loss efforts.
When you concentrate on creating a number of healthy, consistent and sustainable daily routines as opposed to creating a number of short-term solutions, you will help your metabolism work better for overall health, energy and long-term well-being.
FAQ’s
1. What is metabolism?
Metabolism is the process by which your body converts the food and drinks you consume into energy. This energy is used for all the things your body does, like breathing, circulating blood, digesting food, moving, thinking, and repairing cells.
2. Can stress also affect our metabolism?
It is true that prolonged stress can have an effect on your hormones, which will result in a change in the entire body system since it will influence how your body stores fat and how it uses energy.
3. How does sleep influence metabolism?
Sleep has a significant impact on metabolism. The reason for this is that, when a person gets adequate sleep, it helps regulate hormone levels, which in turn controls how the body stores and utilises energy, regulates appetite and helps to maintain a stable level of blood sugar. A lack of enough sleep will slow down the body’s metabolic rate, increase appetite and make it harder to maintain a healthy weight. With enough quality sleep, a person’s body is able to use energy as efficiently as possible.
4. Are metabolic disorders common?
Yes, metabolic disorders are common. Changes in diet and lifestyle are increasingly affecting people both physically and mentally, leading to conditions such as diabetes and thyroid disorders
5. Can diet alone change metabolism?
Your food gives your body the nutrients it needs, like protein for muscle repair and energy that lasts, which helps your metabolism. But food works best when used along with healthy habits like exercise, sleep, and frequent sleep. If you don’t do any of these, especially sleep, your body will use energy less effectively. Your body works best when all of these things are in balance.
6. Can metabolism slow down with age?
As you age, your metabolism starts slowing down. Because with increasing age, your body starts losing muscle, and there are hormonal changes.
7. Does exercise improve metabolism?
Exercise can increase a person’s metabolic rate (the calories that are burned) during physical activity and create an “afterburn” effect where the metabolic rate remains elevated for hours after completing a workout. Strength training increases the amount of muscle a person has, which increases the resting metabolic rate (RMR) and is beneficial for weight management.

